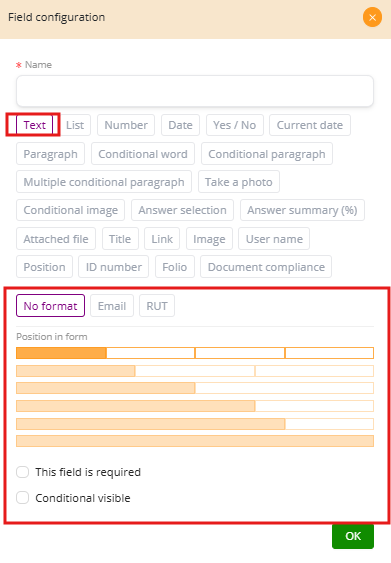
Text Field Configuration #
The Text Field is designed for short, free-form input such as names, email addresses, or identification numbers. It includes three validation formats:
-
No format
-
Accepts any kind of text, including letters, numbers, and special characters.
-
Useful for general information where no restrictions are required.
-
Example:
-
Valid input:
John Doe -
Valid input:
Office 456 – New York
-
-
-
Email
-
Ensures the input follows a valid email structure (user@domain.com).
-
If the input does not include the “@” symbol or a domain, the field will reject it.
-
Example:
-
Valid input:
user@example.com -
Invalid input:
userexample.com
-
-
-
RUT (Chile)
-
Validates the Chilean National ID, including its check digit.
-
If the number or check digit is incorrect, the system prevents submission.
-
Example:
-
Valid input:
12.345.678-9 -
Invalid input:
12345678-0
-
-
The field also allows adjusting position in form using yellow bars. These bars define how much horizontal space the field takes:
-
Example: First Name (50%) + Last Name (50%) → appear side by side.
-
Example: Address (100%) → occupies the entire row.
Two additional options are available:
-
This field is required: The form cannot be submitted if this field is empty.
-
Example: If “Email” is required, leaving it blank will display an error such as “This field is required.”
-
-
Conditional visible: The field only appears if a rule is met.
-
Example: A “Passport number” field appears only if the user selects “Foreign” as nationality.
-
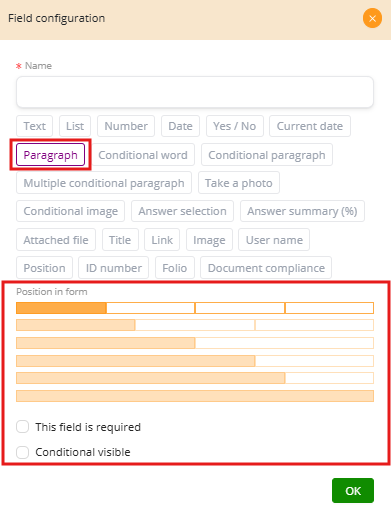
Paragraph Field #
The Paragraph Field is designed for longer text input. Unlike the Text Field, which is used for short data such as names or identification numbers, the Paragraph Field allows users to write full sentences or multiple paragraphs. It is especially useful when forms need detailed explanations, observations, or legal clauses.
This field is commonly used in contracts, agreements, or support forms, where participants must provide additional details.
Example Uses #
-
In a contract template, the paragraph field may capture a full clause such as:
“The tenant agrees to maintain the property in good condition and comply with all local regulations.” -
In a support request form, it could be used for detailed issue descriptions:
“Please describe the problem you are experiencing, including error messages, steps to reproduce, and expected results.”
Position in Form #
The yellow bars define the width of the field in a row.
-
Example: If set to 100%, the field occupies the entire row, which is the most common setting for long text.
This Field is Required #
When enabled, the form cannot be submitted unless the paragraph is completed.
-
Example: A field named “Describe the incident” is required in an insurance claim form.
Conditional Visible #
The field can be configured to appear only under certain conditions.
-
Example: A field “Additional comments” may only appear if the user selects “Other” as the reason for the request.
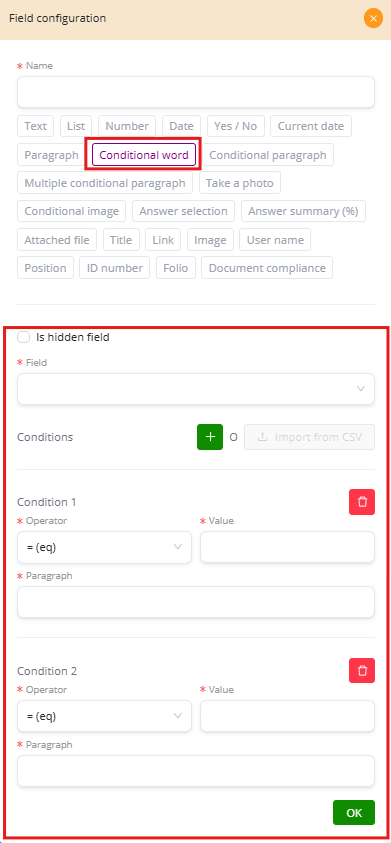
Conditional Word #
The Conditional Word field allows you to insert a word or short phrase that only appears when a specific condition is met. This makes the document dynamic without requiring manual edits.
Configuration Steps #
-
Select the field to evaluate: You can choose from existing fields in the form, such as Name, RUT, Age, Email.
-
Define conditions: Each condition is made up of:
-
Operator: equals (=eq), not equal (!=neq), greater than (>gt), greater or equal (>=gte), less than (<lt), less or equal (<=lte), contains.
-
Value: The expected input that triggers the condition.
-
-
Insert the word or phrase: Write the word or short text that will appear when the condition is satisfied.
Examples #
-
Approval field:
-
Condition: If “Approval” = Yes → Show “Approved”.
-
Condition: If “Approval” = No → Show “Rejected”.
-
-
Gender field:
-
Condition: If “Gender” = Male → Show “Mr.”
-
Condition: If “Gender” = Female → Show “Ms.”
-
-
Age field:
-
Condition: If “Age” > 18 → Show “Adult”
-
Condition: If “Age” < 18 → Show “Minor”
-
Additional Options #
-
Is hidden field: Allows you to hide the field in the final form but still apply logic behind the scenes.
-
Multiple conditions: You can add more than one condition to evaluate different cases.
Conditional Paragraph #
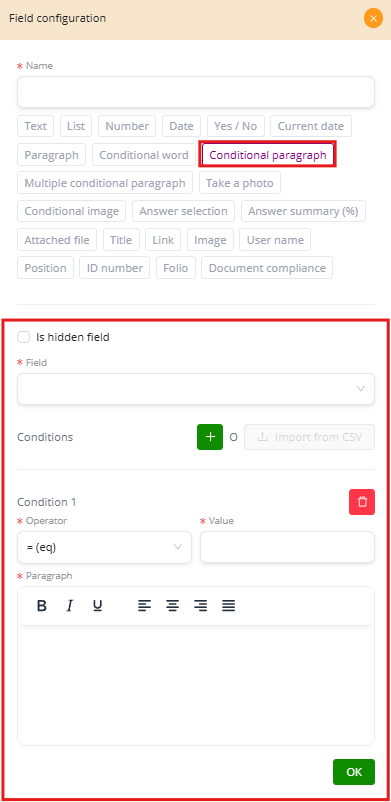
The Conditional Paragraph field works in the same way as the Conditional Word but is used for longer text blocks. Instead of inserting just one word or phrase, it allows you to display entire paragraphs only when a specific condition is satisfied.
How It Works #
-
Select the field to evaluate: Choose from existing form fields, such as Payment Method, Age, Nationality, Approval.
-
Set a condition: Define the operator (equals, not equal, greater than, contains, etc.) and the value that will trigger the condition.
-
Write the paragraph: Enter the full text that should appear when the condition is true.
Examples #
-
Payment clause:
-
Field: Payment Method
-
Condition: If Payment Method = “Installments”
-
Paragraph displayed:
“An additional 2% interest will be applied to each installment payment.”
-
-
Legal clause for foreign clients:
-
Field: Nationality
-
Condition: If Nationality = “Foreign”
-
Paragraph displayed:
“Foreign clients must provide a copy of their passport and residency permit before signing the contract.”
-
-
Age restriction:
-
Field: Age
-
Condition: If Age < 18
-
Paragraph displayed:
“The participant must be accompanied by a legal guardian for all activities.”
-
This field is especially powerful in contracts and agreements because it eliminates the need to create multiple versions of the same document. Instead, the document adapts to the user’s answers.
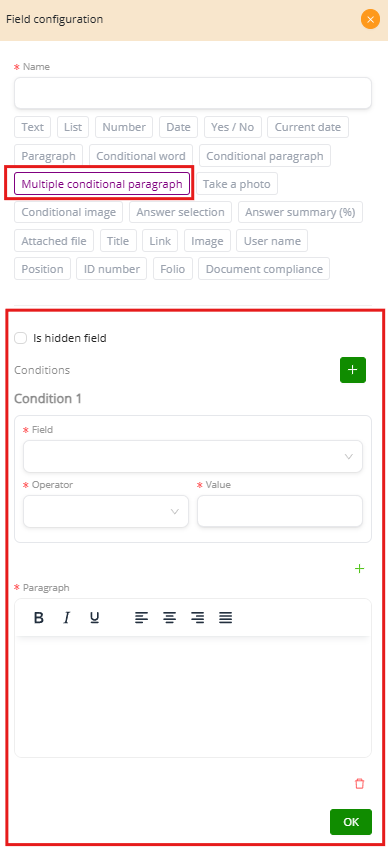
Multiple Conditional Paragraph #
The Multiple Conditional Paragraph field provides more flexibility by allowing several conditions in the same field, each connected to its own paragraph. Instead of creating multiple conditional paragraph fields, you can define different rules in a single place.
How It Works #
-
Select the field to evaluate: Choose from form fields such as Client Type, Age, Payment Method, Nationality.
-
Add multiple conditions: Each condition includes a field, an operator (equals, not equal, greater than, less than, contains, etc.), and a value.
-
Write the paragraph for each condition: When the rule is satisfied, the system will display the corresponding paragraph.
Examples #
-
Client type in contracts:
-
If Client Type = Individual → Paragraph: “This agreement applies to natural persons only.”
-
If Client Type = Company → Paragraph: “This agreement applies to legal entities duly registered in Chile.”
-
If Client Type = Government → Paragraph: “This agreement applies to public sector institutions and is subject to additional compliance requirements.”
-
-
Payment method:
-
If Payment Method = Transfer → Paragraph: “The payment must be made in a single transfer to the designated account.”
-
If Payment Method = Installments → Paragraph: “An additional 2% interest will apply to each installment.”
-
This field is especially useful in contracts, policies, or forms where multiple scenarios must be covered in a single template, making the document adaptive and avoiding duplication.